Utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope’s advanced capabilities, astronomers have provided an unprecedented glimpse into the formation of a newborn star within the Taurus Molecular Cloud. The image reveals a detailed protoplanetary disk and jet activity, offering valuable insights into the early stages of star and planetary system development.
Tag: Star Formation
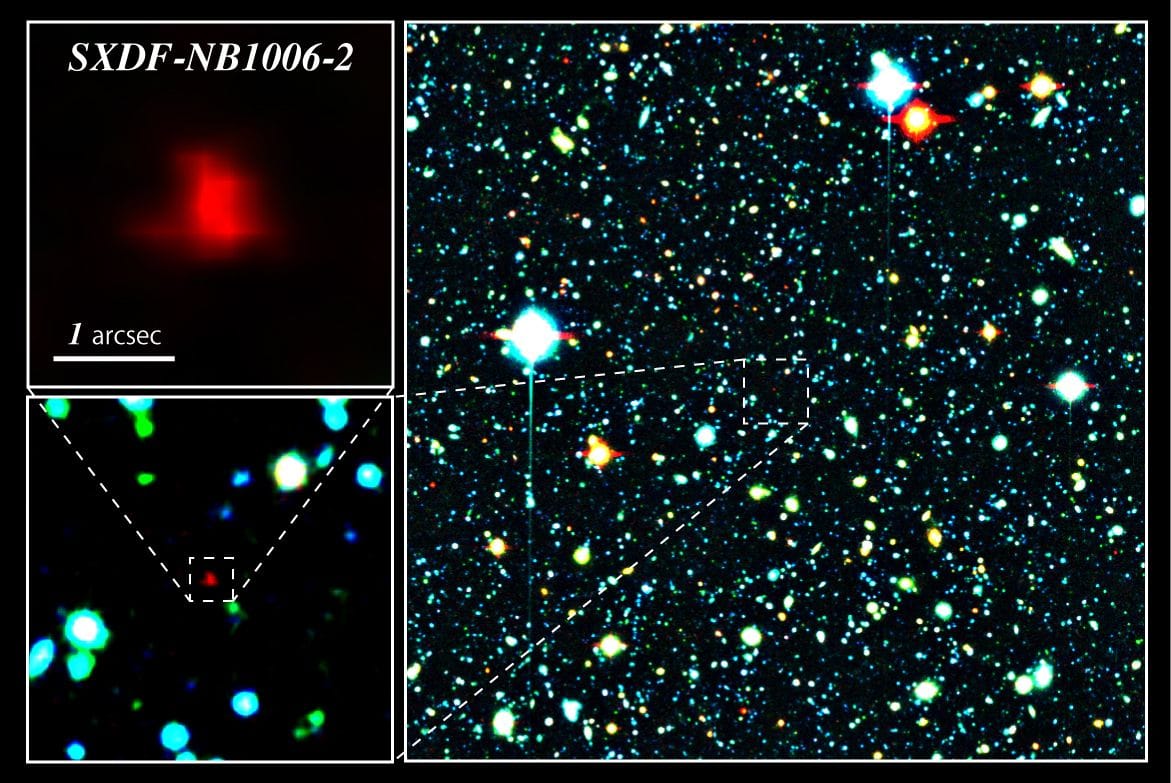
NASA’s Webb Telescope Uncovers Complex Structures of Interstellar Dust and Gas
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has provided unprecedented insights into the intricate layers of interstellar dust and gas, revealing the complex structures that play a crucial role in star formation and the evolution of galaxies. This groundbreaking research enhances our understanding of the universe’s composition and the processes that govern cosmic phenomena.
NASA’s Webb Telescope Uncovers Complex Structures of Interstellar Dust and Gas
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has provided unprecedented insights into the intricate layers of interstellar dust and gas, revealing the complex structures that play a crucial role in star formation and the evolution of galaxies. This groundbreaking research enhances our understanding of the universe’s composition and the processes that govern cosmic phenomena.
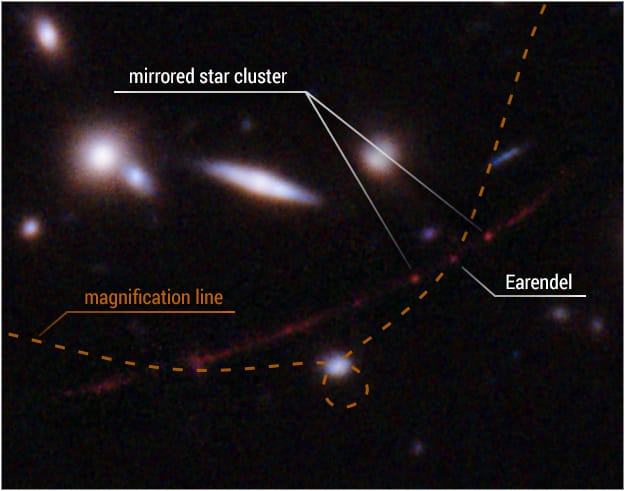
Astronomers Uncover 44 New Stars in Distant Galaxy Through Gravitational Lensing
In a groundbreaking discovery, astronomers have identified 44 new stars in a distant galaxy by utilizing the phenomenon of gravitational lensing. This technique, which involves the bending of light from background objects by massive foreground galaxies, has allowed researchers to peer deeper into the cosmos than ever before. The findings not only enhance our understanding of stellar formation but also provide new insights into the structure and evolution of galaxies.
Astronomers Uncover 44 New Stars in Distant Galaxy Through Gravitational Lensing
In a remarkable discovery, astronomers have identified 44 new stars in a distant galaxy by utilizing the phenomenon of gravitational lensing. This technique, which involves the bending of light from distant objects by massive celestial bodies, has allowed researchers to gain insights into the formation and composition of stars that would otherwise remain hidden from view. The findings not only enhance our understanding of the universe but also demonstrate the potential of gravitational lensing as a powerful tool in modern astronomy.
Astronomers Unveil 44 New Stars in Distant Galaxy Through Gravitational Lensing
A team of astronomers has successfully identified 44 new stars in a distant galaxy by utilizing the phenomenon of gravitational lensing. This method, which involves the bending of light from distant objects due to the gravitational field of an intervening massive object, has enabled researchers to gain insights into the formation and evolution of stars in galaxies far beyond our own. The findings contribute significantly to our understanding of cosmic structures and the behavior of light in the universe.
Astronomers Unveil 44 New Stars in Distant Galaxy Through Gravitational Lensing
A recent astronomical study has revealed the discovery of 44 new stars in a distant galaxy, facilitated by the phenomenon of gravitational lensing. This technique, which involves the bending of light from distant objects by massive celestial bodies, has allowed researchers to observe and analyze previously hidden stellar formations. The findings not only expand our understanding of star formation in the universe but also demonstrate the potential of gravitational lensing as a powerful observational tool in modern astronomy.
Astronomers Unveil 44 New Stars in Distant Galaxy Through Gravitational Lensing
Recent advancements in astronomical techniques have led to the discovery of 44 new stars in a distant galaxy, utilizing the phenomenon of gravitational lensing. This method allows scientists to observe objects that are otherwise too faint or far away to detect. The findings, which enhance our understanding of star formation and galaxy evolution, were made possible by the collaboration of various observatories and the application of sophisticated imaging technologies.