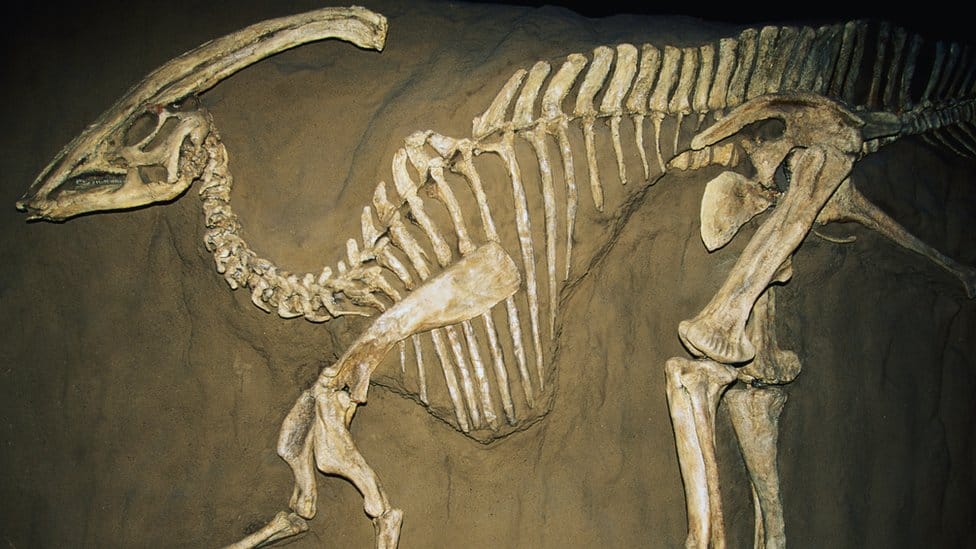
A 68-million-year-old fossil unearthed in Antarctica provides groundbreaking evidence of waterfowl existence dating back to the age of dinosaurs. This discovery not only places modern waterfowl’s origins in the Cretaceous period but also highlights their survival through Earth’s mass extinction events.
Tag: Fossils
Fossilized Stomach Contents Reveal Insights into Cretaceous Diet
An amateur fossil hunter in Montana recently unearthed a remarkable discovery: fossilized stomach contents dating back 66 million years. The find, which consists of regurgitated material from a large theropod dinosaur, provides paleontologists with valuable information about the diet and digestive processes of these prehistoric creatures.
Prehistoric Fossil Discovery: 66 Million-Year-Old Vomit Uncovered in Denmark
Paleontologists in Denmark have made a unique discovery with the unearthing of fossilized vomit, dating back approximately 66 million years. This remarkable find offers insights into the diet and health of ancient creatures that roamed the Earth during the late Cretaceous period.
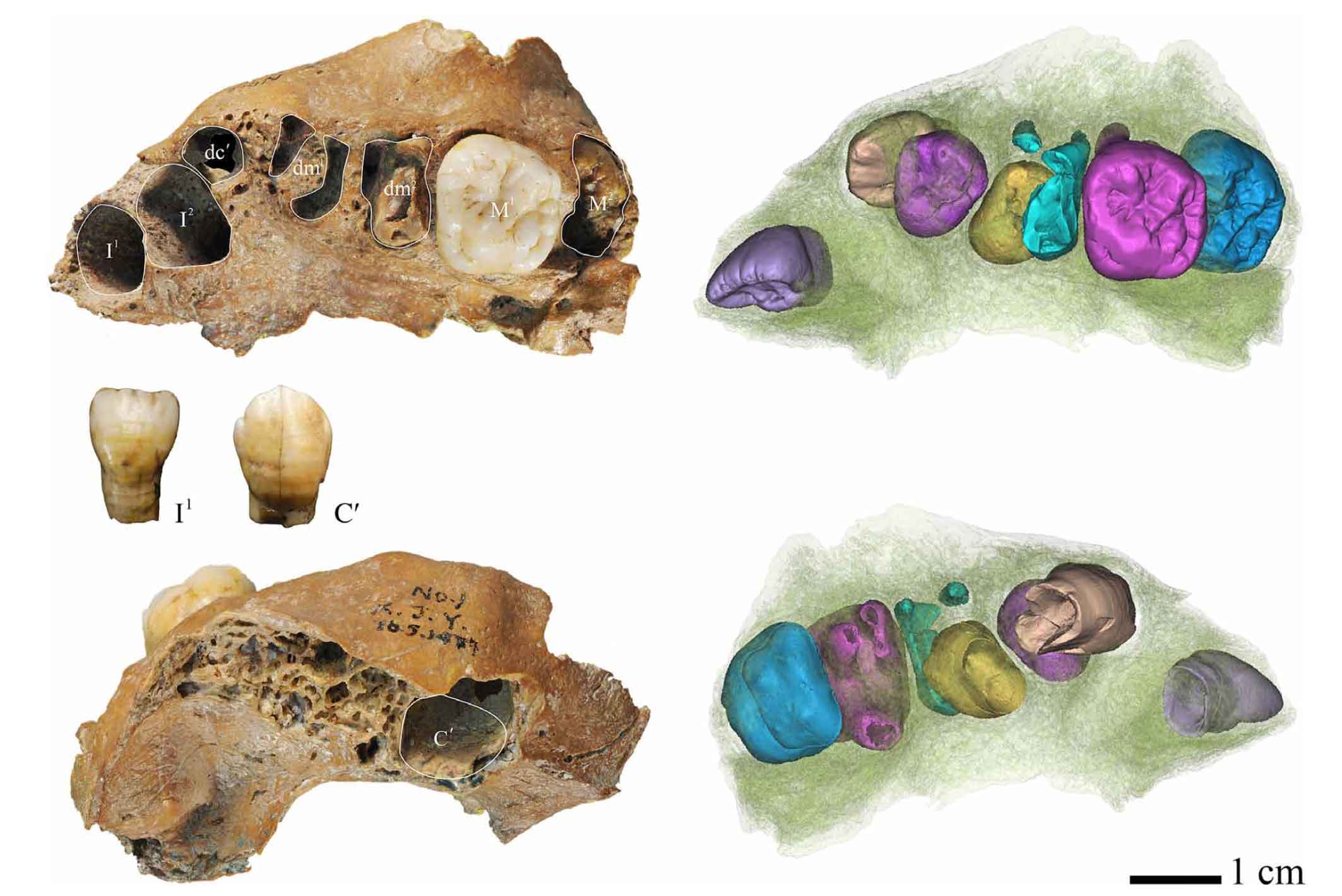
Puzzling Fossil Discovery Traces New Branch in Human Family Tree
Potentially groundbreaking fossils found in China suggest the existence of a previously unknown branch in the human family tree, according to a team of international researchers.
Unearthing Evolution: Unique Fossils Shed Light on Human Ancestry
Rare fossil finds in China may redefine our understanding of the human family tree. A recent discovery suggests a previously unknown branch in human evolution.
New Fossil Discoveries Reveal Potential Human Ancestral Lineage in China
Archaeologists in China have made a groundbreaking discovery of ancient fossils, which may reshape our understanding of human evolution. The findings, discovered in a remote region of the country, indicate the potential presence of an unidentified species related to human ancestry.
Ancient Fossils Discovered in China Suggest New Human Ancestor
Recent fossil discoveries in China have revealed a new species of early human, potentially adding a new branch to the human family tree. The fossils, dated to around 80,000 years ago, exhibit a mix of both modern human and archaic features, providing insights into the complex evolutionary history of our species.
Chinese Fossil Discoveries Prompt Reevaluation of Human Lineage
Recent fossil discoveries in China are prompting scientists to reconsider current understandings of the human family tree. These findings, which include skeletal remains, exhibit a unique combination of features not readily categorized within existing hominin groups. The analysis of these fossils may suggest a previously unknown branch in human evolution, offering new insights into the complex history of our species.
Pre-War Photographs Reveal Undescribed Dinosaur Species
Analysis of archival photographs taken before World War II has led to the identification of a previously unknown dinosaur species. The photographs, which depict fossil remains discovered during an expedition in the early 20th century, provided crucial anatomical details that were not apparent in the physical specimens, allowing paleontologists to classify the bones as belonging to a new genus and species. This discovery highlights the importance of historical records in scientific research and offers new insights into the diversity of prehistoric life.
Chinese Fossil Discovery Sparks Debate on Human Ancestry
Recent fossil discoveries in China are prompting scientists to reconsider the existing understanding of human evolution. The fossils, which include cranial and skeletal remains, exhibit unique characteristics not typically found in known hominin species. This has led to speculation that these remains may represent a previously unknown branch of the human family tree, potentially altering established evolutionary narratives. Further analysis and research are underway to determine the precise placement of these fossils within the human lineage.