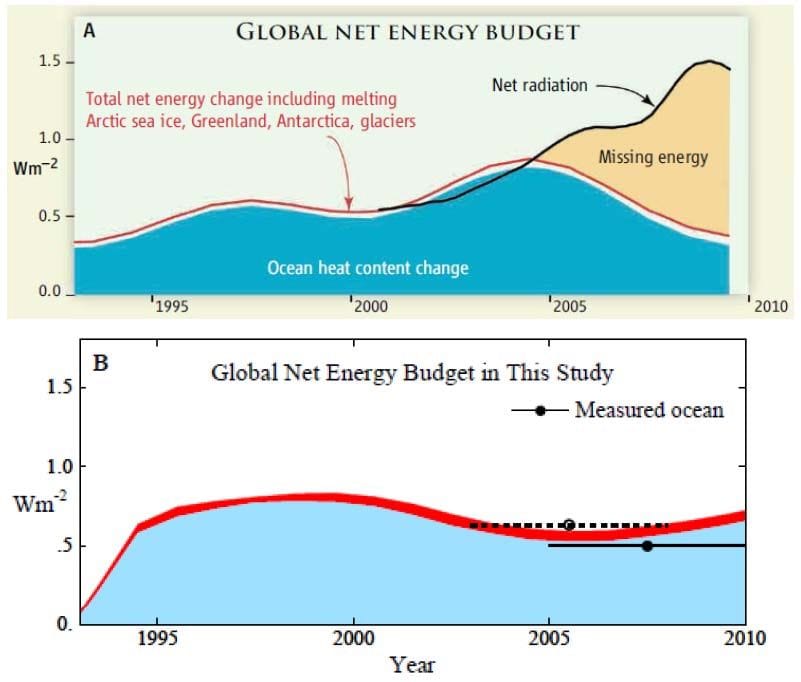
In recent years, scientists have been observing a troubling trend: the Earth’s energy imbalance is increasing at a rate far beyond prior predictions. This phenomenon, where the amount of energy absorbed by the Earth exceeds the amount of energy it emits back into space, has far-reaching implications for global climate and environmental stability. Despite extensive research into the components of Earth’s energy system, the underlying causes of this rapid change remain elusive.
To understand the implications of this energy imbalance, it is essential to grasp the concept of Earth’s energy balance itself. The Earth receives energy primarily from the sun, and this energy is critical for maintaining the planet’s climate and ecosystems. In a stable energy balance, the incoming solar energy approximately matches the outgoing energy reflected back into space. However, this equilibrium is now being disrupted.
According to recent studies, data gathered from satellite observations indicate that the Earth is absorbing significantly more energy than it is able to radiate back into space. This shift is measurable by an increase in the planet’s heat content, particularly in the oceans, which are absorbing over 90% of the excess energy. Current estimates suggest that the energy imbalance is now increasing by about 0.5 watts per square meter per decade, a rate much higher than previous models had anticipated.
Researchers have aptly raised alarms regarding the consequences of this accelerated energy imbalance. Increased heat content in the oceans leads to warmer water temperatures, which can disrupt marine ecosystems, contribute to coral bleaching, and intensify extreme weather events. Additionally, the rising temperatures can exacerbate patterns of sea level rise, potentially displacing communities and affecting coastal economies.
The pathway to a better understanding of these accelerating trends is hindered by the uncertainties surrounding their causes. Many scientists initially attributed shifts in energy balance to human-induced climate change, particularly the increase in greenhouse gas emissions. While this theory remains valid, it falls short of explaining the current rate of change. The interactions among greenhouse gases, clouds, aerosols, and natural climate variability introduce complexities that continue to challenge researchers.
One area of focus for scientists has been the role of clouds. Low- and mid-altitude clouds reflect sunlight back into space, which can influence energy balance significantly. Changes in cloud cover or cloud properties, potentially induced by climate change, may affect how much solar energy is absorbed or reflected. Additionally, it has been hypothesized that the melting of polar ice could lead to changes in heat absorption in these regions, as ice reflects solar energy, while darker ocean water absorbs it.
Another contributing factor could be changes in ocean circulation patterns. These patterns regulate heat distribution throughout the globe. Variability in these currents could lead to uneven heating and consequently influence the overall energy balance. Again, the exact mechanisms remain poorly understood, leading to significant gaps in knowledge and understanding.
The scientific consensus emphasizes the need for robust models that incorporate various interacting factors to create a clearer picture of what is influencing this alarming energy imbalance. Building such comprehensive models is paramount to improving climate predictions and formulating strategies for mitigation. Enhanced observation systems, improved satellite technologies, and interdisciplinary research are critical components of this effort.
In addition, international collaboration among scientists and policymakers is vital. The effects of accelerated energy imbalance are global in nature, crossing national boundaries and impacting regional climates. Fostering dialogue and cooperation among scientists can promote the sharing of data and insights across borders, thereby accelerating the pace of discovery.
While uncertainty may cloud the understanding of the causes behind this rapid increase in Earth’s energy imbalance, one fact remains clear: the consequences are potentially severe and widespread. As governments, organizations, and citizens grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, enhancing our understanding of energy dynamics should be viewed as a priority.
Efforts toward global emissions reductions must continue in earnest to curb greenhouse gas output while further research is conducted on the complexities surrounding Earth’s energy balance. An informed, science-based approach is imperative to adapt to the realities of climate change and safeguard the planet for future generations.
In conclusion, the acceleration of the Earth’s energy imbalance highlights a critical juncture in our understanding of climate science. The urgent need for answers calls for collaborative research endeavors, innovative technology, and a commitment to unraveling this complex and pressing issue. As data continues to emerge, it will play a crucial role in shaping global energy policies and climate action strategies, guiding the world toward a more sustainable and resilient future.