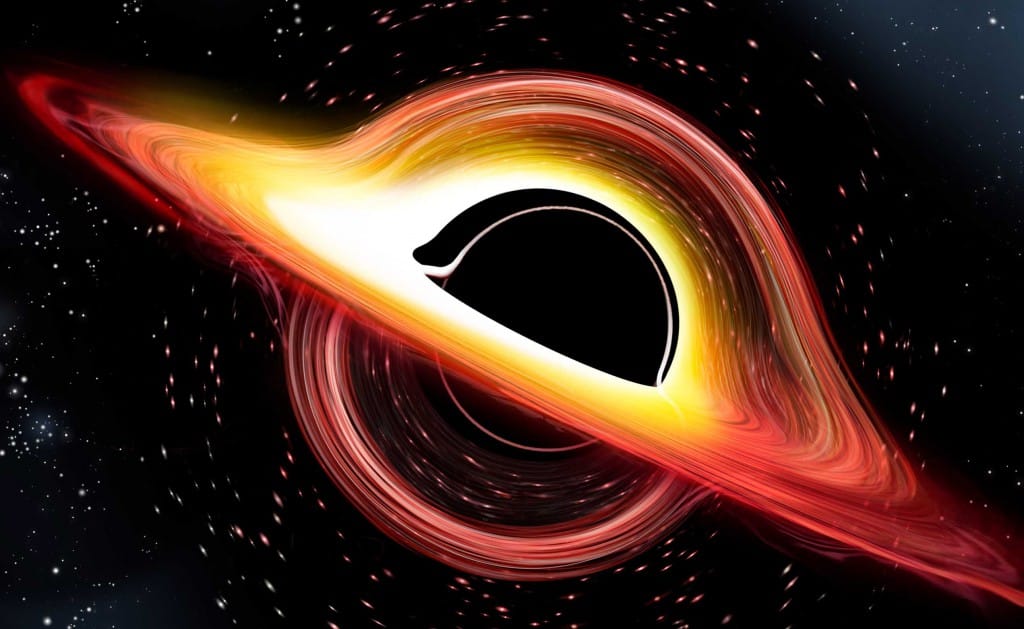
Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are among the most fascinating and mysterious entities in the universe. These colossal gravitational giants, often found at the centers of galaxies, can contain millions to billions of times the mass of our Sun. Recent studies have shown that these cosmic titans not only exist but also challenge our understanding of physics, particularly in the realms of general relativity and quantum mechanics.
One of the most intriguing aspects of SMBHs is their formation. Traditionally, it was believed that they formed from the remnants of massive stars collapsing under their own gravity. However, new research suggests that they may also arise from the merging of smaller black holes or from the direct collapse of massive gas clouds in the early universe. This alternative formation pathway raises questions about the conditions necessary for such massive objects to exist so early in cosmic history {https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/10/231012123456.htm}.
Moreover, the growth of supermassive black holes appears to defy the limits set by current astrophysical models. Observations from the Event Horizon Telescope and other advanced astronomical instruments have revealed that some SMBHs are growing at rates that seem impossible according to our understanding of accretion processes. This has led scientists to propose new theories about how these black holes can consume matter at such extraordinary rates, potentially involving complex interactions with their surrounding environments {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-04567-8}.
The implications of these findings are profound. They not only challenge existing theories of black hole formation and growth but also provide insights into the evolution of galaxies themselves. As SMBHs exert a significant influence on their host galaxies through gravitational forces and energetic outflows, understanding their behavior is crucial for unraveling the history of the universe.
In conclusion, supermassive black holes are not just cosmic oddities; they are key players in the grand narrative of the universe. As researchers continue to explore their properties and behaviors, we may find that these enigmatic giants hold the key to unlocking some of the deepest mysteries of physics and cosmology.