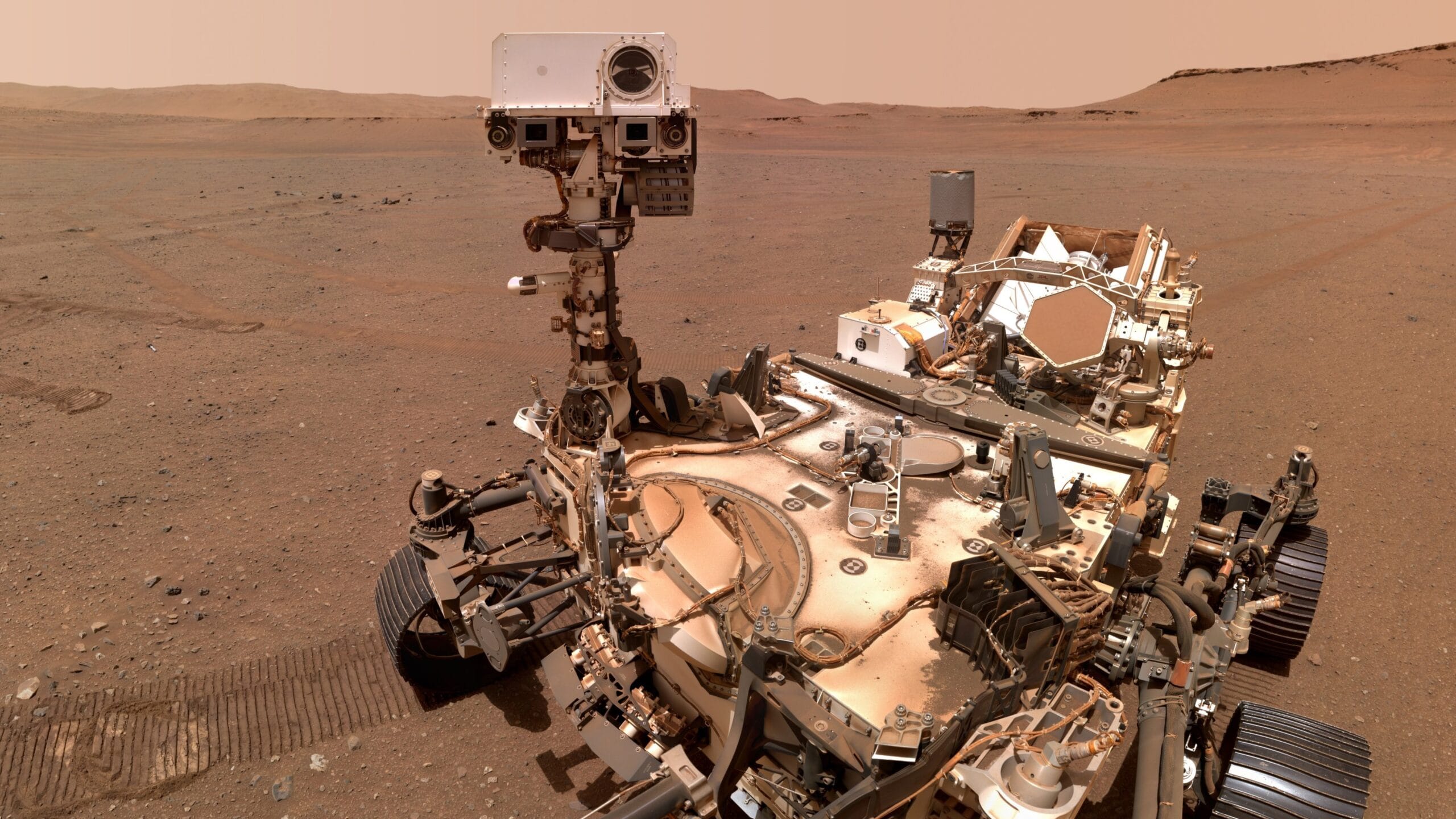
NASA’s Perseverance rover has recently achieved a significant milestone in its exploration of Mars by successfully navigating a giant crater, a feat that highlights the rover’s advanced technology and the meticulous planning that went into its mission. Launched on July 30, 2020, Perseverance landed on the Martian surface on February 18, 2021, with the primary goal of searching for signs of ancient microbial life and collecting samples for future return missions to Earth.
The crater, known as Jezero Crater, is approximately 28 miles (45 kilometers) wide and was chosen as the landing site due to its unique geological features and the presence of a delta, which is believed to have formed from ancient river activity. This area is of particular interest to scientists, as it may hold clues about the planet’s climate history and its potential to harbor life.
Navigating the crater presented various challenges for the Perseverance rover. The rugged terrain, characterized by steep slopes, loose rocks, and dust-covered surfaces, required the rover’s advanced autonomous navigation systems to carefully assess its surroundings and make real-time decisions. The rover is equipped with sophisticated cameras and sensors that allow it to identify hazards and plot safe routes, enabling it to traverse the crater efficiently.
As Perseverance made its way through the crater, it conducted a series of scientific observations and experiments. One of the rover’s key instruments, the SuperCam, was utilized to analyze the composition of Martian rocks and soil, providing insights into the planet’s geological history. The rover also employed its PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry) to determine the elemental makeup of the materials it encountered, which can reveal information about past environmental conditions.
In addition to geological analysis, Perseverance is also tasked with searching for biosignatures—indicators of past life. The rover’s Mars Sample Return mission aims to collect rock and soil samples that will eventually be returned to Earth for further study. This ambitious endeavor is a collaboration between NASA and the European Space Agency and is expected to provide unprecedented insights into the history of Mars and the possibility of life beyond our planet.
The successful navigation of the crater is not only a testament to the engineering prowess behind the Perseverance rover but also to the collaborative efforts of scientists and engineers working on the mission. Each decision made during the rover’s journey is grounded in years of research and planning, aimed at maximizing the scientific return from this exploration.
As Perseverance continues its journey, it is expected to encounter additional geological features that will further enrich our understanding of Mars. The rover’s ability to adapt to varying terrain and conditions is crucial for its ongoing mission. Scientists are closely monitoring the data transmitted back to Earth, which will inform future exploration strategies and enhance our understanding of Martian geology.
The findings from Perseverance’s navigation through the crater are anticipated to contribute to a broader narrative about Mars’ past and its potential for supporting life. The data collected will be analyzed by scientists around the world, who will work to piece together the planet’s history and its evolution over billions of years.
In conclusion, the successful navigation of the giant Martian crater by NASA’s Perseverance rover marks a significant achievement in the ongoing exploration of Mars. The rover’s advanced technology and autonomous capabilities have enabled it to traverse challenging terrain while conducting vital scientific research. As the mission progresses, the insights gained from Perseverance’s exploration will continue to deepen our understanding of Mars and its potential to have once harbored life.