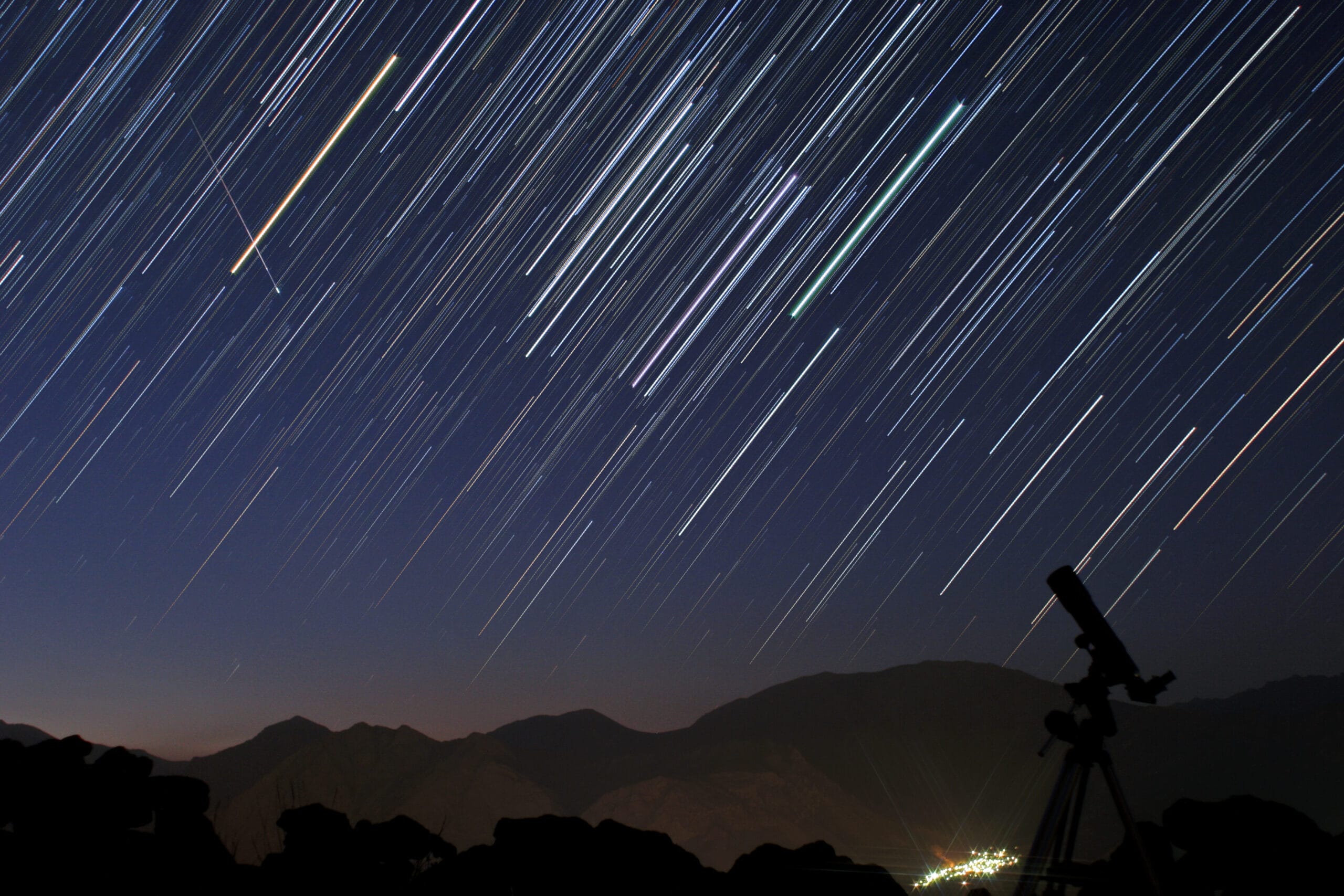
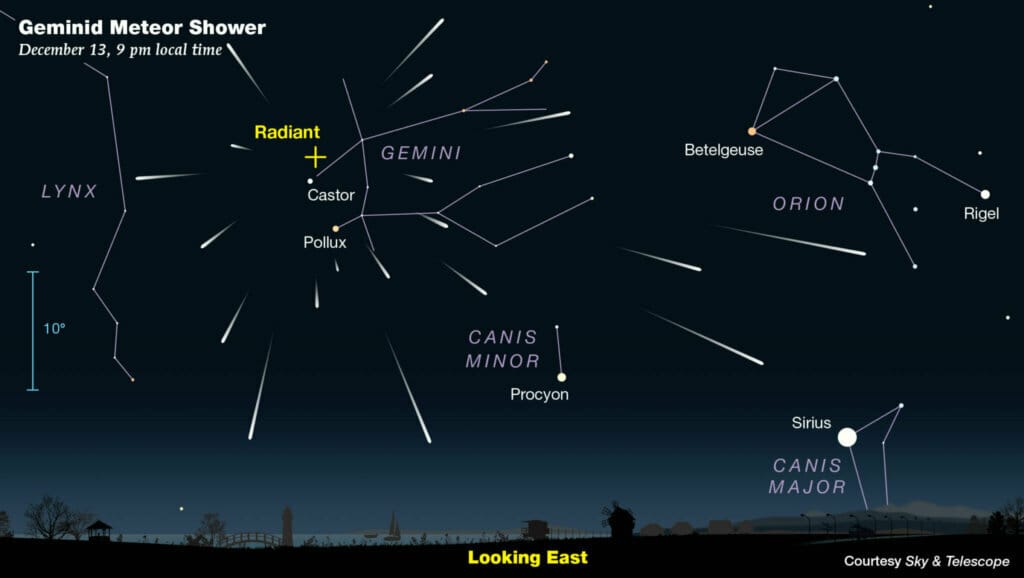
The Geminid meteor shower is one of the most anticipated astronomical events of the year, captivating stargazers with its stunning display of meteors. This year, the shower is expected to peak during the night, offering an excellent opportunity for both amateur and seasoned astronomers to witness its brilliance. The Geminids, which occur annually from December 4 to December 17, are particularly notable for their bright fireballs, making them a favorite among meteor enthusiasts.
The origins of the Geminid meteor shower can be traced back to the asteroid 3200 Phaethon, which is considered a “rock comet.” Unlike most meteor showers that originate from comets, the Geminids are unique in that they are associated with an asteroid. As Earth passes through the debris trail left by 3200 Phaethon, particles enter the atmosphere at high speeds, resulting in the spectacular display of meteors.
For those eager to catch a glimpse of the Geminids, timing is crucial. The best viewing conditions are typically found in the early hours before dawn, specifically between midnight and 4 a.m. local time. During this period, the radiant point of the shower, located in the constellation Gemini, is highest in the sky, allowing for optimal visibility. However, meteors can be seen in all parts of the sky, so viewers should position themselves in an area with minimal light pollution for the best experience.
Weather conditions also play a significant role in meteor shower visibility. Clear skies are essential for observing meteors, as clouds can obstruct the view. As the peak approaches, forecasts indicate whether the sky will be clear or if clouds will hinder visibility. It is advisable for viewers to check local weather reports leading up to the peak night to plan accordingly.
In addition to weather, the moon phase can impact viewing conditions. A bright moon can wash out fainter meteors, making it challenging to see the full spectrum of the shower. This year, the moon will be in a waning gibbous phase, which means it will be visible in the sky but will not be at its brightest. This phase should allow for a good viewing experience, as the moonlight will not completely overpower the meteors.
For those who wish to enhance their viewing experience, finding a dark location away from city lights is essential. National parks, rural areas, and elevated locations often provide the best vantage points. It is advisable to arrive early to allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness, which can take up to 30 minutes. Bringing along a reclining chair or blanket can also make for a more comfortable viewing experience.
While the Geminids are known for their high meteor count, it is important to note that not all meteors will be equally bright. The shower is expected to produce around 120 meteors per hour at its peak, but this number can fluctuate based on various factors, including local atmospheric conditions and light pollution. Observers may notice a range of meteors, from faint streaks to bright fireballs that can illuminate the night sky.
In addition to the visual spectacle, the Geminid meteor shower provides a unique opportunity for scientific research. Astronomers study meteor showers to gain insights into the composition of the solar system and the processes that shape celestial bodies. Each meteor that burns up in the atmosphere leaves behind a trail of ionized gas, which can be analyzed to learn more about the materials that make up asteroids and comets.
As the Geminid meteor shower approaches its peak, it serves as a reminder of the beauty and wonder of the universe. Stargazers are encouraged to take the time to step outside, look up at the night sky, and enjoy the show. With the right preparation and conditions, the Geminids can provide a memorable experience that connects observers to the cosmos.
In conclusion, the Geminid meteor shower is set to peak this week, providing an exciting opportunity for sky watchers to witness one of nature’s most spectacular displays. By understanding the best times to view, considering weather and moon conditions, and finding a suitable location, observers can maximize their chances of experiencing the brilliance of this celestial event. As the night unfolds, the sky may come alive with meteors, each one a fleeting reminder of the dynamic universe we inhabit.