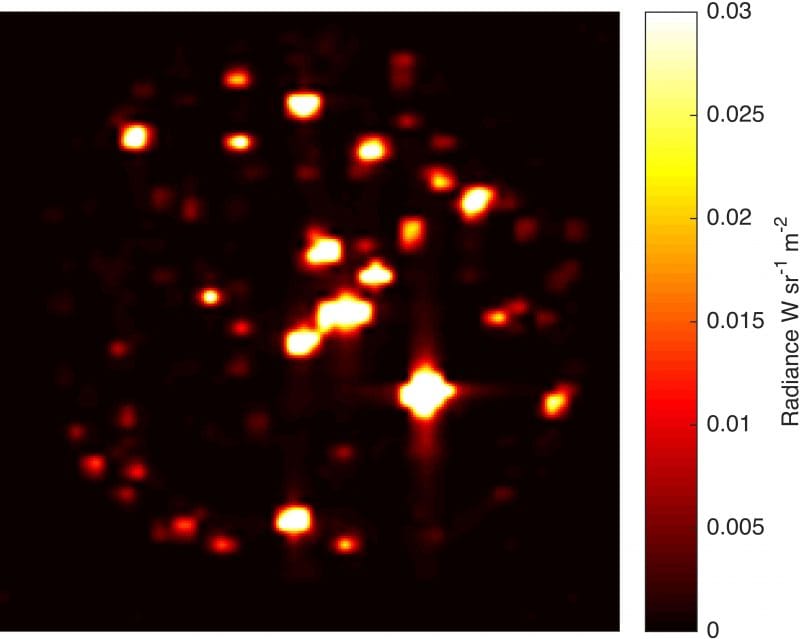
The study of celestial bodies in our solar system often leads to fascinating discoveries that enhance our understanding of planetary science. One of the most intriguing subjects of research is Io, one of Jupiter’s largest moons, renowned for its extreme volcanic activity. Recent observations have shed light on the processes that govern its geology, addressing questions that have lingered since the Voyager 1 mission in 1979.
Io stands out among the solar system’s moons due to its remarkable volcanic landscape. It is the most geologically active body in the solar system, with hundreds of volcanoes, some of which are continuously erupting. This volcanic activity is primarily driven by tidal heating, a process that occurs due to the gravitational pull exerted by Jupiter and the other Galilean moons—Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. As Io orbits Jupiter, the gravitational forces cause significant flexing of its interior, generating heat that fuels its volcanic eruptions.
The recent observations have been facilitated by the Juno spacecraft, which has been studying Jupiter and its moons since its arrival in 2016. Juno’s advanced instruments have allowed scientists to gather data on Io’s surface composition and thermal activity, providing a clearer picture of the moon’s geological processes. This data is crucial for understanding how Io’s volcanic activity compares to that of other celestial bodies, such as Earth and Venus.
One of the key findings from Juno’s observations is the identification of specific materials on Io’s surface that are indicative of its volcanic activity. The presence of sulfur and other compounds suggests that Io’s eruptions are not only frequent but also diverse in their chemical composition. These findings align with earlier data collected by the Galileo spacecraft, which orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003 and provided the first detailed images of Io’s surface.
The study of Io’s volcanoes has implications beyond understanding its geology; it also offers insights into the potential for life in extreme environments. While Io’s surface is inhospitable due to its intense radiation and high temperatures, the subsurface ocean hypothesis for other moons, such as Europa, raises questions about the conditions that might support life elsewhere in the solar system. Understanding the geological processes on Io can help scientists draw comparisons with other celestial bodies that may harbor life.
In addition to the volcanic activity, Juno’s observations have also highlighted the interaction between Io and Jupiter’s magnetosphere. The intense radiation environment around Jupiter affects Io’s surface and atmosphere, leading to complex chemical reactions that contribute to the moon’s unique characteristics. This interaction is a focal point for researchers aiming to understand the broader implications of planetary atmospheres and magnetospheres in our solar system.
The findings from Juno and previous missions have sparked renewed interest in Io, prompting scientists to consider future missions that could further explore its geology and potential for habitability. The data collected thus far has laid the groundwork for understanding the intricate balance of forces that shape Io’s surface and drive its volcanic activity.
As researchers continue to analyze the data from Juno and other missions, the mysteries surrounding Io may gradually be unraveled. The ongoing exploration of this volcanic world not only enriches our understanding of the solar system but also highlights the importance of continued investment in planetary science. By studying celestial bodies like Io, scientists can gain insights into the processes that govern planetary evolution, which may one day inform our understanding of exoplanets in distant star systems.
In conclusion, the recent observations of Io have provided valuable information that contributes to our understanding of this unique moon. The volcanic activity on Io, driven by tidal heating and influenced by its interactions with Jupiter, presents a captivating subject for ongoing research. As scientists continue to investigate the geological processes at play, they will undoubtedly uncover more about the complexities of our solar system and the potential for life in extreme environments.