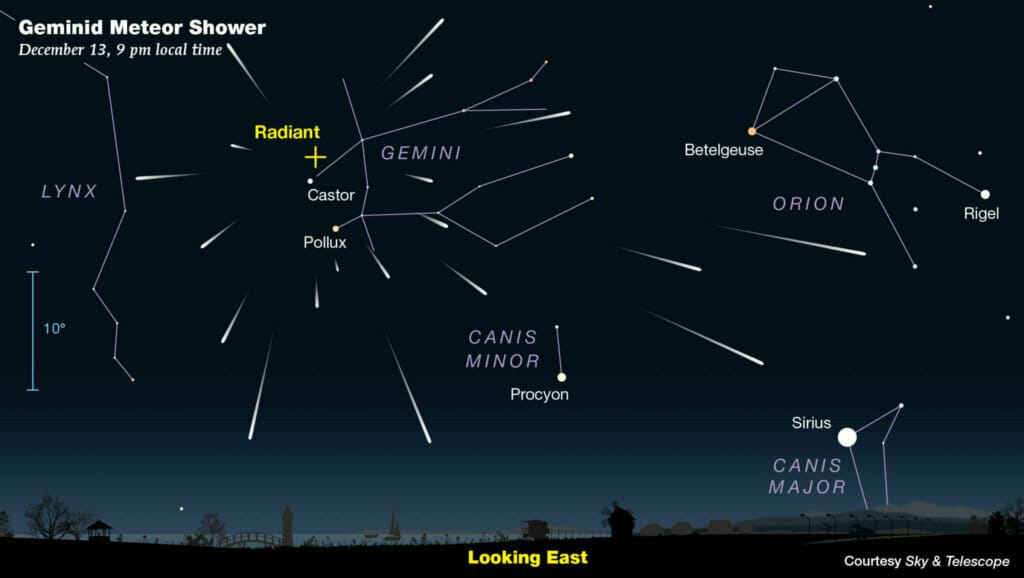
The Geminid meteor shower is one of the most anticipated astronomical events of the year, renowned for its dazzling displays of shooting stars. Occurring annually in December, the shower is characterized by its bright and colorful meteors, which can sometimes appear as fireballs due to their speed and size. This year, the Geminids are expected to peak on the night of December 13 into the early morning hours of December 14, offering an excellent opportunity for enthusiasts and casual observers alike to witness this natural spectacle.
The Geminid meteor shower is unique compared to other meteor showers, primarily because it originates from the asteroid 3200 Phaethon, rather than a comet. This distinction is significant because while comets shed ice and dust, asteroids like Phaethon leave behind rocky debris. When Earth passes through this debris, the particles enter our atmosphere at high speeds, typically around 70 kilometers per second, creating the bright streaks of light we see as meteors.
Observers can expect to see upwards of 120 meteors per hour at the peak of the shower, making the Geminids one of the most prolific meteor showers of the year. The meteors can come in a variety of colors, often appearing white, yellow, blue, or even red, depending on the composition of the particles. The Geminids are also notable for their slow-moving meteors, which allows viewers to enjoy the beauty of the display for longer than other showers.
To maximize the viewing experience, it is essential to choose the right location. Ideal spots for observing the meteor shower are areas away from city lights and light pollution. Rural areas or parks with open skies are preferable. Additionally, finding a location with a clear view of the horizon in all directions can enhance the experience, as meteors can appear anywhere in the sky.
Timing is also crucial for optimal viewing. The best time to observe the Geminid meteor shower is generally between midnight and dawn, when the sky is darkest and the meteor activity is at its highest. However, meteors can be seen as early as 9 PM, though they will be fewer in number. It is recommended to allow the eyes to adjust to the darkness for at least 20 minutes, which will enhance the ability to see faint meteors.
Weather conditions play a significant role in the viewing experience as well. Clear skies are ideal, and it is wise to check local weather forecasts ahead of time. Clouds, rain, or snow can obstruct visibility, making it difficult or impossible to see the meteors. Observers should also consider the moon’s phase; a full moon can create additional light pollution, making it harder to see the fainter meteors. This year, the moon will be in its waxing gibbous phase, which means it will rise later in the night, improving visibility during the peak hours.
For those unable to view the Geminid meteor shower in person, many organizations and observatories often provide live streams of the event. This allows anyone with internet access to experience the shower from the comfort of their home. These streams typically feature experts who provide commentary on the meteor shower, offering insights into the science behind the phenomena and tips for viewers.
In conclusion, the Geminid meteor shower is a spectacular event that captures the interest of skywatchers around the world. With its peak occurring on the night of December 13 into December 14, enthusiasts should prepare by selecting a suitable viewing location and checking the weather conditions. Whether observed in person or through a live stream, witnessing the Geminids promises to be a memorable experience, celebrating the beauty of our universe.