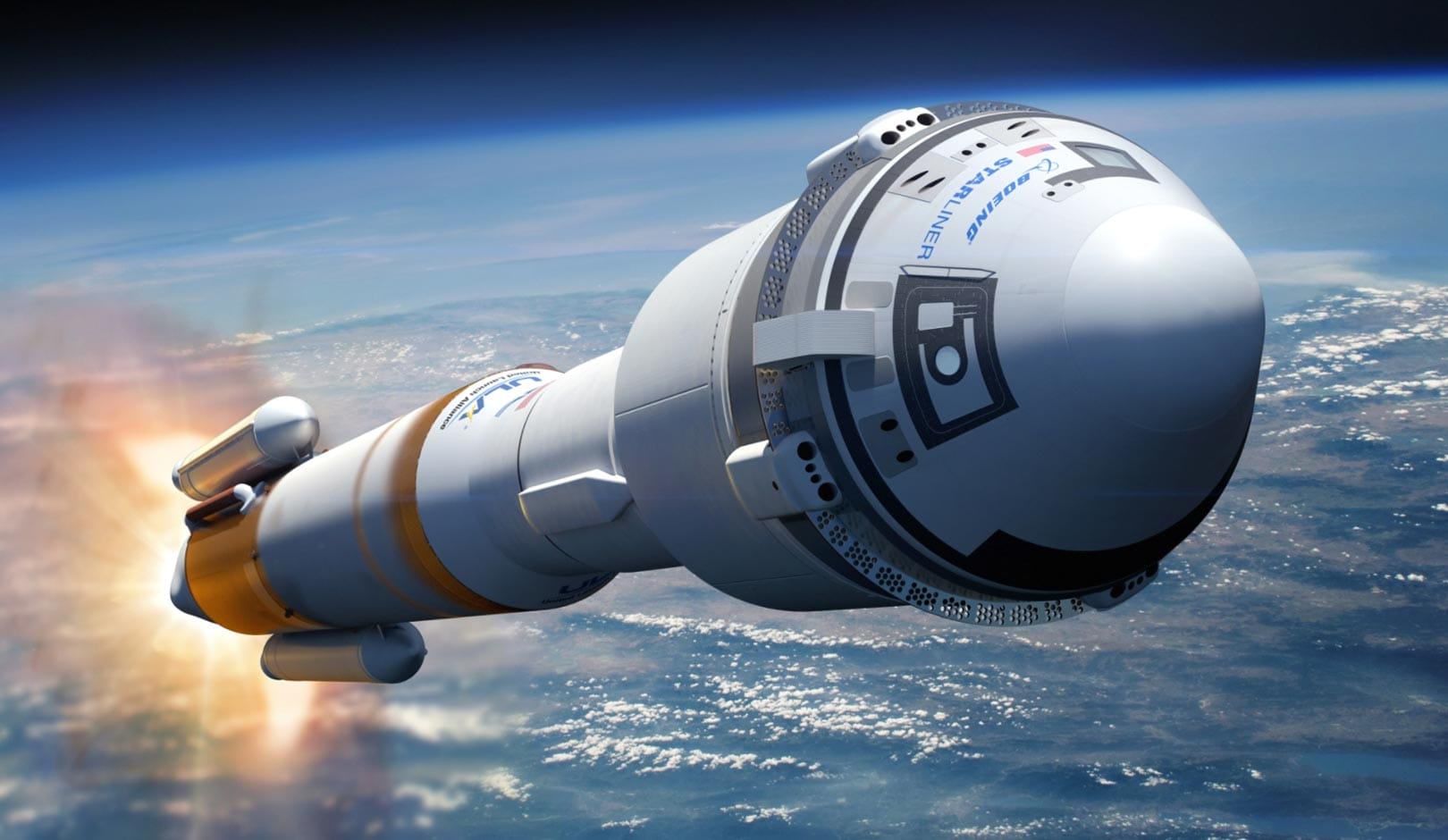
Boeing has announced that the return of crewed missions aboard its Starliner spacecraft, initially projected for earlier this year, has been postponed until March. This delay is part of ongoing efforts to address an array of technical challenges that have arisen in the lead-up to these significant missions, which are seen as crucial for both the company and the broader objectives of NASA.
The Boeing Starliner, developed through NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, is designed to ferry astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS). It represents a critical component of the United States’ strategy to secure a reliable transportation system to the orbiting laboratory, particularly in the wake of the Space Shuttle’s retirement in 2011. Since that time, the United States has relied on Russian Soyuz spacecraft to transport astronauts, which has underscored the importance of achieving operational flights through local capabilities provided by companies like Boeing and SpaceX.
Despite extensive testing and preparations, the announcement of the delay reflects the complexity associated with human spaceflight. Boeing has faced a number of engineering and scheduling challenges throughout the development process, leading to increased scrutiny of its plans. The company has been diligently working to address these issues, prioritizing safety and thoroughness above expedience.
In prior missions, such as the uncrewed Orbital Flight Test (OFT-1) in December 2019, the spacecraft experienced significant technical difficulties. In particular, issues with the spacecraft’s timing system prevented it from concluding its mission as planned. These setbacks have prompted Boeing to take a more cautious approach to ensure that all systems function as intended before crewed flights commence.
The updated timeline suggests that Boeing could potentially perform integrated tests and evaluations in early 2024, allowing for a thorough assessment of the spacecraft’s systems in a crewed configuration. This will also include safety reviews and other critical preparations to mitigate risks associated with sending astronauts into space. NASA officials have expressed their acknowledgment of the delay as a necessary step to ensure the reliability and safety of the Starliner program.
In addition to technical challenges, the ongoing global supply chain issues have also impacted Boeing’s production timelines. These challenges have reverberated across many sectors of the aerospace industry, contributing to delays in various components required for the spacecraft’s final assembly and testing phases. As such, Boeing continues to coordinate closely with suppliers and partners to address these disruptions, demonstrating a commitment to mitigate the impact on overall project timelines.
The return of the Starliner crewed mission is highly anticipated not only by officials at Boeing and NASA but also by the broader scientific community and public. The successful operation of the Starliner is intended to pave the way for future NASA initiatives, including lunar exploration missions as part of the Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon by 2024.
Despite the setbacks, officials remain hopeful that the revised timeline will ultimately lead to successful crewed missions. The stakes are high, and both Boeing and NASA are focused on delivering a spacecraft that performs reliably and meets safety standards. As the preparations move forward, there will be cautious optimism within the aerospace sector regarding the progress of the Starliner program.
While the adjustments to the timeline present challenges, they also present opportunities for learning and improvement within the aerospace industry. Boeing’s experience with the Starliner program may provide valuable insights that could inform future projects and help enhance overall safety protocols in human spaceflight.
As March approaches, Boeing will continue to prepare for an eventual crewed flight, maintaining a clear focus on performance, safety, and adherence to technical standards. It is essential that the Starliner successfully demonstrates its capabilities to provide ongoing transport to the ISS, ensuring that NASA can continue its critical missions in low-Earth orbit.
The delay serves as a reminder of the inherent complexities involved in human space exploration. With every advancement comes a thorough examination of technology, processes, and procedures, making it clear that meticulous preparation and robust testing are key to the success of future missions.
As the aerospace community watches closely, all eyes will be on Boeing as it works to meet the new target of a crewed Starliner mission in March. The anticipated flights promise to be a milestone in the ongoing saga of commercial human spaceflight and will have lasting implications for both Boeing’s legacy in aerospace and NASA’s strategic goals for exploration.