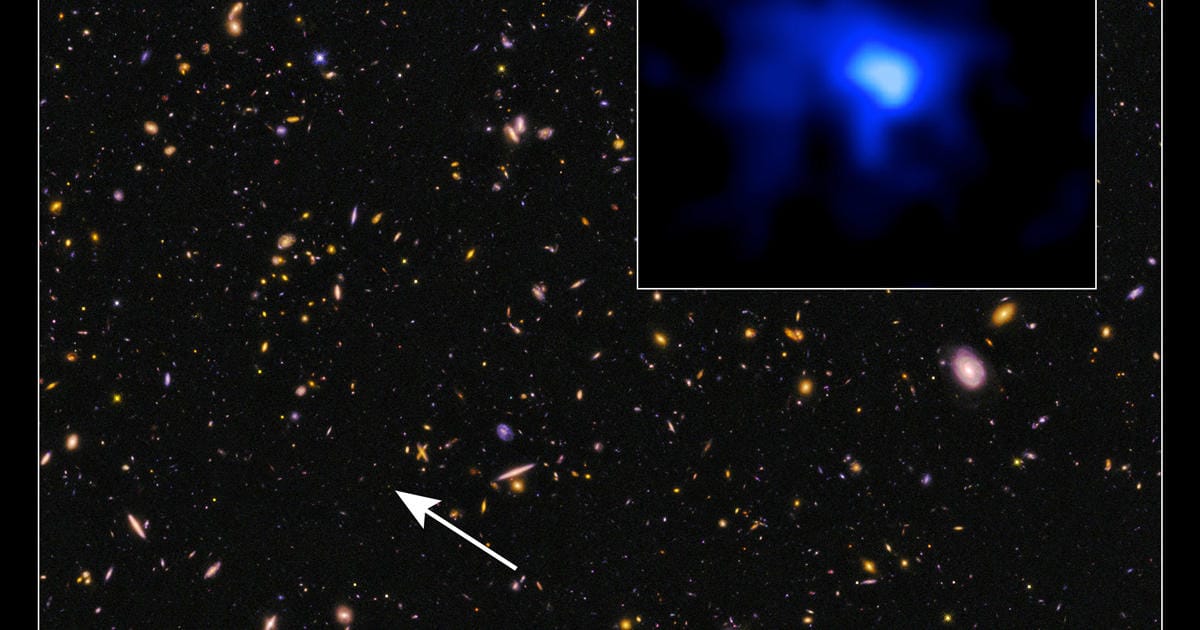
Using the intriguing phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, a team of astronomers has made an extraordinary discovery: 44 new stars that were previously hidden from our view in a distant galaxy. These celestial bodies have been revealed due to the unique properties of gravitational lensing, a result of the curvature of spacetime caused by massive objects. By making use of this extraordinary astrophysical phenomenon, scientists have managed to observe distant celestial objects that were previously beyond their reach.
The deflection of light caused by massive bodies such as galaxies or clusters of galaxies acts as natural telescopes, magnifying and distorting light from objects located far behind them. This effect, known as gravitational lensing, enables us to see distant sources that would normally be invisible due to their high redshift or extreme distances. By identifying fluctuations in the gravitational field of massive foreground objects, astronomers have been able to detect otherwise unobservable light sources.
The team of astronomers identified 44 new stars in a distant galaxy using the unique characteristic of gravitational lensing, which represents a breakthrough in the field of astronomy. These findings will allow scientists to study the distant galaxy, its structure, and its stellar composition in greater detail and with new perspectives.
The discovery of 44 new stars lurking behind a distant galaxy sheds light on the vastness of the cosmos. Despite the enormous distances and complex interactions at play, scientific inquiry continues to reveal a richer, more textured understanding of the universe. Gravitational lensing has proven to be a powerful and indispensable tool for astronomers seeking to unveil the secrets of the cosmos.