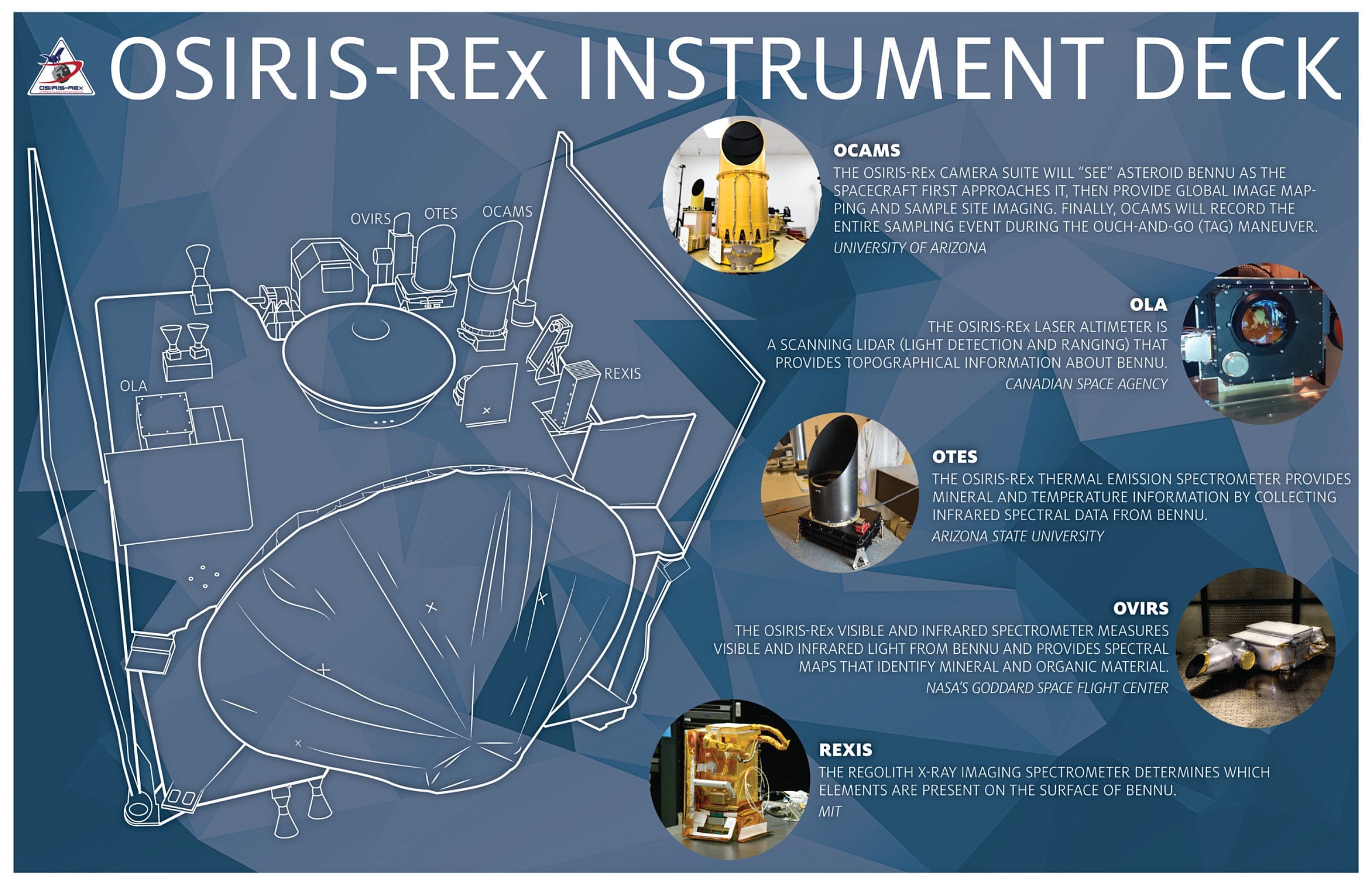
The OSIRIS-REx mission, a groundbreaking endeavor by NASA, has yielded remarkable results with the analysis of samples collected from the asteroid Bennu. The spacecraft, launched in 2016, successfully touched down on the asteroid’s surface in 2020 and collected a substantial sample of regolith, which was returned to Earth in 2023. Initial analysis of this precious cargo has revealed the presence of organic molecules within the asteroid’s composition. These organic molecules are complex carbon-based compounds, considered essential components in the formation of life as we know it. The discovery is not definitive proof of extraterrestrial life, but it represents a substantial leap forward in our understanding of the potential for life’s origins beyond our planet.
The presence of these organic molecules on Bennu, a carbonaceous asteroid, suggests that the building blocks of life may have been widely distributed throughout the early solar system. This raises the intriguing possibility that similar molecules may have been delivered to early Earth via asteroid impacts, potentially contributing to the emergence of life. The scientific community is particularly excited about this discovery because it provides tangible evidence supporting the hypothesis that the necessary ingredients for life were not unique to Earth. Further research is underway to fully characterize the identified organic molecules and determine their exact composition. Scientists are employing a range of sophisticated analytical techniques to dissect the complex chemical makeup of the sample, including chromatography and mass spectrometry. These techniques will allow researchers to identify specific types of organic molecules and determine their relative abundances. This detailed analysis will provide crucial insights into the processes that led to the formation of these molecules within the asteroid.
The OSIRIS-REx mission’s success is a testament to the ingenuity and dedication of the scientists and engineers involved. The mission represents a significant investment in space exploration and has already yielded invaluable data. The careful planning and execution of the sample return, along with the meticulous analysis of the sample, have resulted in a groundbreaking scientific discovery. This achievement underscores the importance of continued exploration of asteroids and other celestial bodies to unravel the mysteries of our solar system and the potential for life beyond Earth. The findings from the Bennu sample analysis are expected to be published in several peer-reviewed scientific journals, allowing the broader scientific community to scrutinize the data and contribute to further research. This collaborative effort will be crucial in fully understanding the implications of this discovery and guiding future space exploration missions. The long-term goal is to deepen our understanding of the origin of life, not only on Earth but potentially elsewhere in the universe. The information gained from the Bennu sample will undoubtedly inform future missions and research strategies, shaping our understanding of planetary formation and the prevalence of organic molecules in the cosmos. The implications extend beyond the scientific community, inspiring future generations to pursue careers in science and technology and fostering a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the universe.
The ongoing analysis of the Bennu sample is expected to produce further significant findings in the coming years. The international collaboration between scientists from various countries underscores the global nature of scientific discovery and the collective pursuit of knowledge. The data collected will be shared openly, fostering further research and collaboration within the scientific community. The discovery of organic molecules on Bennu is a major step forward in our quest to understand the origin and prevalence of life in the universe. It emphasizes the importance of continued investment in space exploration and the pursuit of scientific knowledge.