The Geminid meteor shower, which occurs every December, is one of the most prominent and reliable meteor showers of the year. It is characterized by its bright, multi-colored meteors that can be seen streaking across the night sky. This year, the meteor shower is expected to peak tonight, providing an exceptional viewing experience for astronomy enthusiasts and casual observers alike.
The Geminids are unique in that they originate from an asteroid rather than a comet, which is the case for many other meteor showers. The asteroid 3200 Phaethon, discovered in 1983, is the source of the Geminid meteors. As Earth passes through the debris field left by this asteroid, particles enter the atmosphere at high speeds, creating the stunning visual spectacle that we associate with meteor showers. The Geminids are known for their bright, fast meteors, which can leave trails that linger in the sky for several seconds.
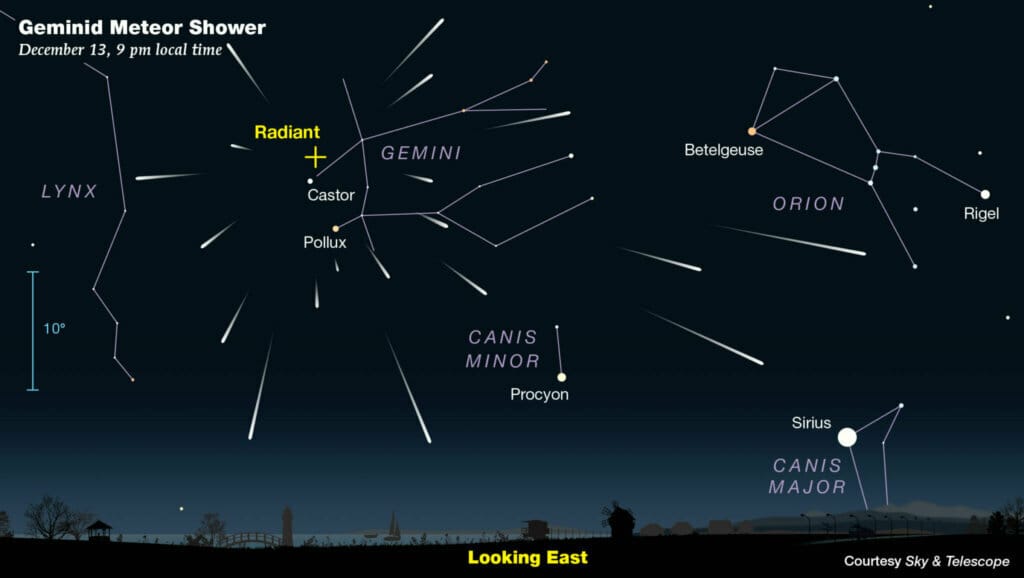
The peak of the meteor shower is expected to occur tonight, with optimal viewing conditions for those in areas with clear skies. Under ideal circumstances, observers can expect to see up to 120 meteors per hour. However, the actual number may vary depending on local weather conditions and light pollution. To maximize the viewing experience, it is advisable to find a dark location away from city lights, where the meteors will be more easily visible against the dark backdrop of the night sky.
Timing is also crucial for viewing the Geminids. The best time to observe the meteor shower is typically after midnight and before dawn when the sky is darkest. However, meteors can be seen as early as 9 PM. It is recommended to allow the eyes to adjust to the darkness for about 20 minutes to enhance visibility. Lying back on a blanket or reclining chair can provide a comfortable viewing position, allowing observers to take in the full expanse of the sky.
The meteors produced by the Geminid shower are known for their diversity in color, ranging from white and yellow to blue and green. This variety is due to the different chemical compositions of the meteoroids. For instance, sodium produces a yellow color, while copper can create a blue hue. This colorful display adds to the allure of the Geminid meteor shower, making it a favorite among both amateur and professional astronomers.
In addition to the visual spectacle, the Geminids provide valuable opportunities for scientific study. Researchers can analyze the composition of the meteoroids, which can offer insights into the early solar system and the materials that formed the planets. The study of meteor showers also helps astronomers understand the dynamics of asteroid belts and the potential hazards posed by near-Earth objects.
The Geminid meteor shower has a rich history, with records dating back to the 19th century. Initially, it was not widely observed, but over the years, it has gained popularity, particularly as advancements in technology have made it easier for people to access information about celestial events. Today, the Geminids are celebrated as one of the most reliable meteor showers, attracting attention from skywatchers around the globe.
As the Geminid meteor shower peaks tonight, it serves as a reminder of the wonders of our universe. Whether you are an experienced astronomer or simply someone looking to enjoy a night under the stars, the Geminids offer a chance to connect with the cosmos. Make sure to prepare for the event by checking local weather forecasts, gathering warm clothing, and finding a suitable viewing location.
In conclusion, the annual Geminid meteor shower is an extraordinary event that captivates audiences with its breathtaking display of meteors. With the peak occurring tonight, stargazers are encouraged to take advantage of this opportunity to witness one of nature’s most beautiful phenomena. By understanding the origins, characteristics, and optimal viewing conditions of the Geminids, everyone can enjoy this celestial celebration to the fullest.