Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) has long been a subject of interest within the medical community. Primarily characterized by issues with focus, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, ADHD affects individuals across the globe. Recently, a growing body of research has emerged, suggesting that ADHD may contribute to a shorter lifespan for those affected. This article explores the potential link between ADHD and reduced life expectancy, examining the factors that may exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD and highlighting key areas for further investigation.
The connection between ADHD and shortened lifespans can be attributed to a wide range of factors. Those with ADHD often struggle with impulsivity, which may increase their risk of engaging in unsafe or high-risk behaviors such as substance abuse, risky sexual activity, or dangerous driving. Furthermore, the high levels of stress and frustration commonly experienced by individuals with ADHD may lead to self-destructive behaviors, exacerbating emotional turmoil and further impacting overall health and well-being.
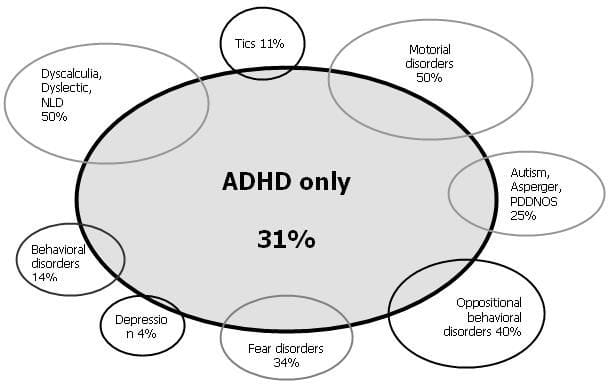
In addition to these concerns, individuals with ADHD are at a higher risk of developing a number of co-occurring health conditions that can have severe, long-term effects on their quality of life and lifespan. For instance, research has consistently shown an increased likelihood of developing eating disorders such as bulimia or anorexia nervosa, as well as conditions such as anxiety and depression in individuals with ADHD. Moreover, those with ADHD often struggle to adhere to medication regimens, which can result in poor medical management of chronic illnesses.
It is also crucial to consider the potential impact of ADHD misdiagnosis and underdiagnosis. In some cases, individuals may be improperly diagnosed or fail to receive a diagnosis altogether, which can prevent them from accessing crucial support and resources. Consequently, this can lead to inadequate management of symptoms and exacerbate existing challenges, further impacting overall health and well-being.
Ultimately, the complex web of factors associated with ADHD demands further attention when it comes to the potential impact on lifespans. As researchers continue to dive deeper into this issue, a better understanding of the connection between ADHD and reduced life expectancy can help inform the development of interventions, therapies, and support systems that can help mitigate these risks and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with ADHD.