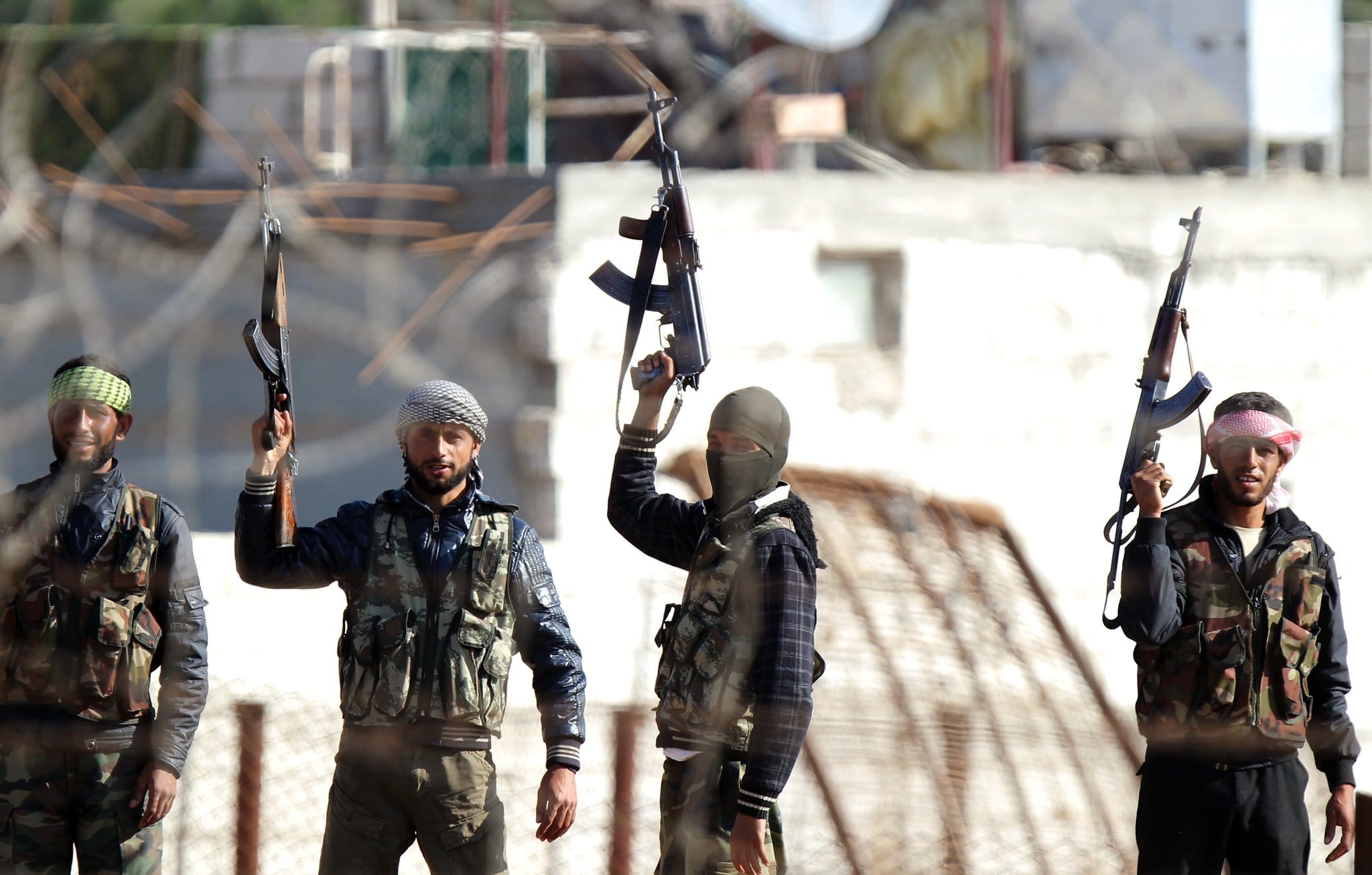
The Syrian civil war has entered a new phase, with rebel forces making significant gains against the government of Bashar al-Assad. The advances have been driven in part by the collapse of government forces in key areas, as well as the influx of foreign fighters and support from external backers.
One of the key factors driving the rebel gains has been the collapse of government forces in the north of the country. In recent weeks, rebel forces have made significant advances in the provinces of Aleppo and Idlib, capturing key towns and cities and pushing government forces back.
The rebel gains have been driven in part by the influx of foreign fighters, who have flocked to Syria to join the fight against the Assad government. Many of these fighters are affiliated with Islamist groups, such as the al-Nusra Front and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIS).
The involvement of Islamist groups in the Syrian conflict has raised concerns among US officials, who fear that these groups could gain control of the country if the rebels are successful in overthrowing the Assad government. US officials have expressed concerns that Islamist groups could establish a new base of operations in Syria, from which they could launch attacks against Western targets.
Despite these concerns, the US has continued to provide support to the rebels, including non-lethal aid and military training. However, the US has also sought to distance itself from the more extremist elements of the rebel movement, and has instead sought to build relationships with more moderate groups.
One of the key challenges facing the US and other external backers of the rebels is the issue of Islamist influence within the rebel movement. While many rebels are motivated by a desire to overthrow the Assad government and establish a more democratic system, others are driven by a desire to establish an Islamist state.
The al-Nusra Front, one of the most prominent Islamist groups fighting in Syria, has been designated as a terrorist organization by the US and other countries. However, the group has also been one of the most effective fighting forces on the rebel side, and has played a key role in many of the rebel victories.
The involvement of Islamist groups in the Syrian conflict has also raised concerns among other countries in the region. Many of Syria’s neighbors, including Jordan and Lebanon, have expressed concerns that the conflict could spill over into their territories, and that Islamist groups could establish a foothold in the region.
Despite these concerns, many countries in the region have continued to provide support to the rebels, including military aid and logistical support. The Gulf states, in particular, have been key backers of the rebels, and have provided significant financial and military support to the movement.
The Syrian government has also sought to exploit the issue of Islamist influence within the rebel movement, and has sought to portray the rebels as being dominated by extremist groups. The government has accused the rebels of being “terrorists” and has sought to justify its own actions as a necessary response to the threat posed by these groups.
However, many observers believe that the government’s claims are exaggerated, and that the rebel movement is more diverse than the government suggests. While it is true that Islamist groups play a significant role in the rebel movement, many rebels are motivated by more secular concerns, such as a desire to overthrow the Assad government and establish a more democratic system.
The conflict in Syria is complex and multifaceted, and there is no easy solution in sight. However, one thing is clear: the involvement of Islamist groups in the conflict has raised concerns among US officials and other external backers of the rebels, and has highlighted the need for a more nuanced and sophisticated approach to the conflict.
In recent weeks, the US has sought to build relationships with more moderate elements of the rebel movement, and has provided support to groups that are seen as being more secular and democratic. However, the US has also sought to maintain a degree of distance from the more extremist elements of the rebel movement, and has expressed concerns about the potential for Islamist groups to gain control of the country.
The US has also sought to work with other countries in the region to address the issue of Islamist influence within the rebel movement. In recent weeks, the US has held talks with countries such as Turkey and Jordan, and has sought to build a coalition of countries that can work together to address the conflict.
Despite these efforts, the conflict in Syria remains complex and multifaceted, and there is no easy solution in sight. However, one thing is clear: the involvement of Islamist groups in the conflict has raised concerns among US officials and other external backers of the rebels, and has highlighted the need for a more nuanced and sophisticated approach to the conflict.