The Federal Reserve’s Monetary Policy Dynamics: A Look Ahead
As the Federal Reserve navigates through the complexities of the current economic landscape, many economists are projecting a final interest rate cut before a significant shift in policy strategy in 2025. This forecast emerges from a close examination of inflation trends, labor market conditions, and overall economic activity, all of which play crucial roles in shaping monetary policy decisions.
### Historical Context
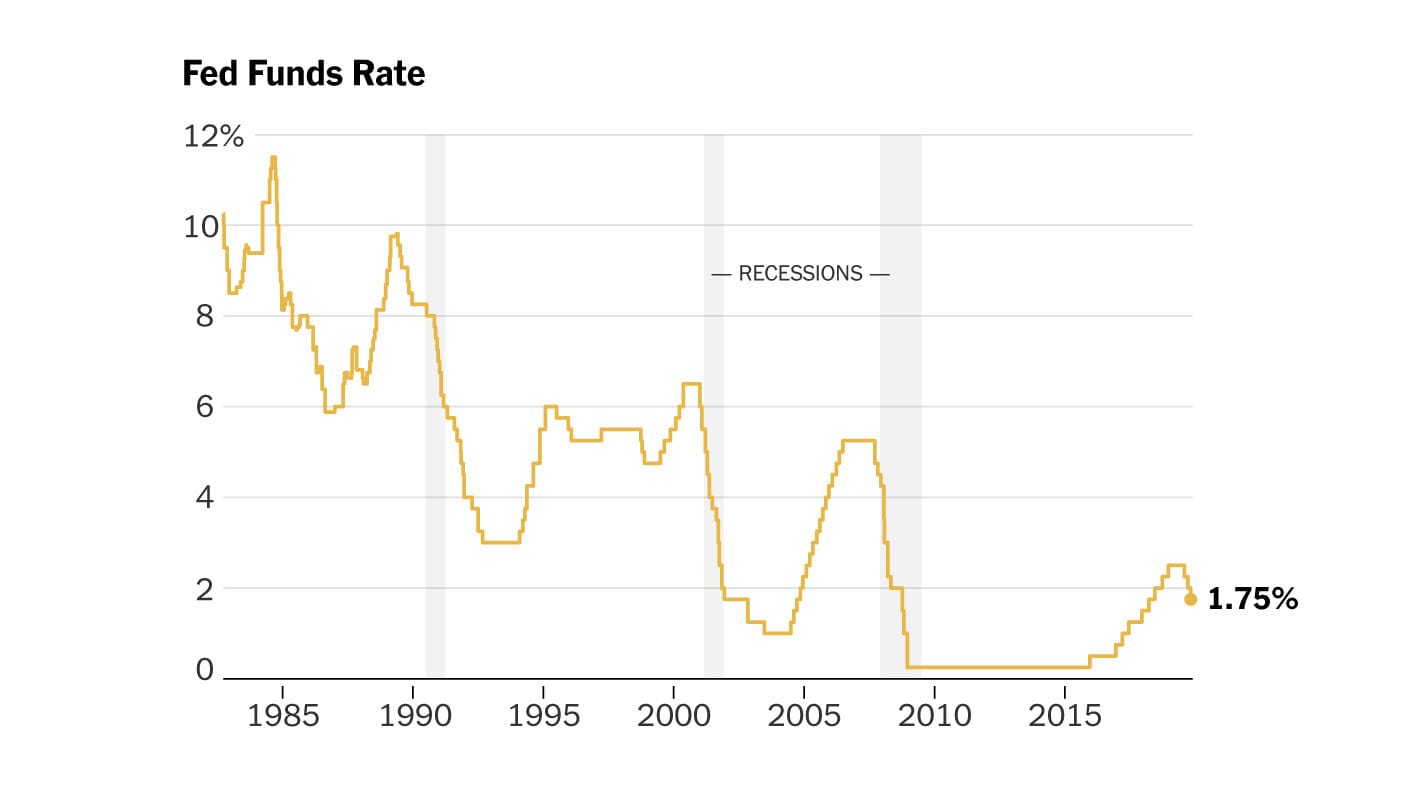
To understand the current expectations regarding the Federal Reserve’s future actions, one must first consider the broader history of U.S. interest rate policy. In response to the financial crisis of 2008, the Fed slashed rates to near-zero levels, aiming to stimulate economic activity. This policy stance remained for several years while the economy gradually recovered. The historical precedent of extended low rates has created residual effects regarding inflation and economic growth that continue to influence current policy.
Over the past two years, the economic landscape has been characterized by a significant post-pandemic recovery. As the economy rebounded, inflation began to rear its head—reaching levels not seen in decades. In response, the Federal Reserve has embarked on an aggressive monetary tightening campaign by increasing interest rates multiple times throughout 2022 and 2023 to combat this inflationary pressure.
### Current Economic Indicators
As of late 2023, inflation, while still elevated, has shown signs of moderation. Recent data indicate that inflation rates are gradually returning toward the Fed’s target of 2%. However, key concerns remain regarding the sustainability of this trend, as other economic indicators present a mixed picture.
#### Inflation Trends
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks changes in the price level of a basket of consumer goods and services, has decreased from its peak but remains higher than historical norms. Many economists argue that closely observing these trends is essential for the Fed as it weighs potential future cuts to interest rates. The interplay between inflation levels and consumer purchasing power will be a deciding factor in shaping the future trajectory of Fed policy.
#### Labor Market Conditions
The U.S. labor market has shown resilience, with unemployment figures remaining low despite economic uncertainties. Job growth has continued, though at a decelerating pace, raising concerns that the labor market may not be able to sustain such growth indefinitely. This factor plays a crucial role in the Fed’s considerations, as higher employment levels generally correlate with increased spending and economic activity, both of which can influence inflation.
#### Economic Activity
It is also critical to examine broader economic indicators, including GDP growth and consumer confidence figures. While GDP growth has exhibited stability, signs of a slowdown are beginning to surface, prompting economists to analyze the potential for a more measured approach from the Fed in the coming years. Any signs of recession could shift the Fed’s priorities towards supporting growth over controlling inflation, leading to the anticipated rate cut before modifying their strategy in 2025.
### The Predictions for 2024
Economists widely expect a final reduction in interest rates in 2024 as the Fed aims to provide a cushion against any economic turbulence while still managing inflation concerns. The timing and extent of this expected cut will hinge upon continued evaluations of economic data, as well as guidance from Fed officials.
The anticipated rate cut is seen as a strategic maneuver to provide further support to the economy, particularly for sectors most sensitive to interest rates, such as housing and consumer lending. Access to affordable credit is critical for sustaining consumer spending, which propels economic growth.
However, the landscape remains fluid. While many analysts predict a final cut, potential risks, including unexpected inflation fluctuations and global economic conditions, could alter that course. The global economy’s interconnectedness means external shocks can have repercussions that influence domestic monetary policy decisions.
### Transitioning to 2025: A New Strategy?
Looking ahead to 2025, the Fed is expected to transition its approach in response to evolving economic conditions. As inflation stabilizes and the economy recalibrates, the emphasis may shift from aggressive rate cuts to a more nuanced strategy focusing on maintaining long-term economic health.
This shift may include a recalibration of the Fed’s dual mandate, which calls for achieving maximum employment and stable prices. The balance between these objectives will remain a central theme in the Fed’s overarching strategy as they endeavor to adapt to any emerging economic realities.
### Conclusion
In summary, the Federal Reserve’s actions in the coming months and years will be closely monitored by economists and market participants alike. While a final interest rate cut is anticipated in 2024, the strategic pivot expected in 2025 will be pivotal in shaping the U.S. monetary policy landscape. Continuing to analyze inflationary pressures, employment dynamics, and overall economic activity will be instrumental in guiding these decisive actions.
As the economy progresses, the Fed’s ability to adapt to changing conditions will be crucial. Stakeholders across multiple sectors—businesses, consumers, and investors—must remain vigilant to understand the potential implications of the Fed’s policy shifts and the broader economic landscape in which these changes occur.
### Moving Forward
Ultimately, staying informed about the Fed’s communications and decisions will be imperative for all economic participants. The path ahead may be uncertain, but the Federal Reserve’s historical commitment to using data-driven decision-making should serve as a solid framework for navigating the challenges ahead.