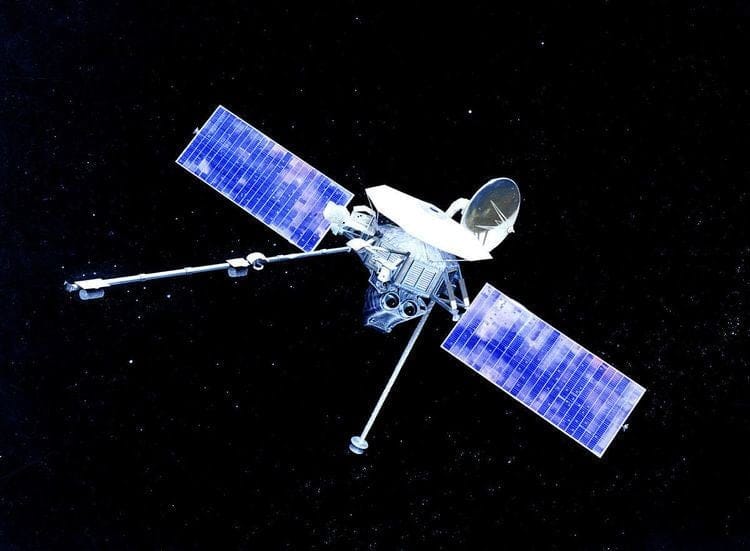
The exploration of Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, has long been a challenging endeavor for scientists and space agencies. Its extreme temperatures, harsh environment, and proximity to the Sun have made it difficult to study in detail. However, a new spacecraft has recently made significant strides in this area, capturing remarkably detailed images of Mercury’s surface that reveal features previously obscured from view.
The spacecraft, launched as part of a mission aimed at studying the inner solar system, has been equipped with state-of-the-art imaging technology. This technology allows for high-resolution photography and data collection, enabling scientists to analyze the planet’s surface with unprecedented clarity. The images captured by the spacecraft showcase a variety of geological features, including craters, ridges, and plains, providing insights into the planet’s formation and evolution.
One of the most significant aspects of this mission is the ability to observe areas of Mercury that were not adequately captured during previous missions, such as NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft, which orbited Mercury from 2011 to 2015. While MESSENGER provided valuable data, its imaging capabilities were limited by the technology available at the time. The new spacecraft, however, has overcome these limitations, allowing for a more comprehensive examination of the planet’s surface.
The detailed images reveal a complex geological history, suggesting that Mercury has undergone significant changes over billions of years. Scientists have noted the presence of large impact craters, which indicate that the planet has been bombarded by asteroids and comets throughout its history. Additionally, the images show evidence of volcanic activity, with smooth plains that may have been formed by ancient lava flows. These findings contribute to a growing body of evidence that Mercury is a geologically active planet, contrary to previous assumptions that it was largely inert.
In addition to geological features, the spacecraft’s observations have also provided insights into Mercury’s atmosphere, or lack thereof. The planet has a very thin atmosphere, primarily composed of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, and potassium. The new data suggests that this tenuous atmosphere is influenced by solar activity, which can strip away particles and affect the planet’s surface conditions. Understanding the interactions between Mercury’s surface and its atmosphere is crucial for comprehending the planet’s overall environment and its potential for hosting life, even in microbial forms.
The mission has also focused on studying Mercury’s magnetic field, which is unique among the terrestrial planets. The spacecraft’s instruments have been able to measure variations in the magnetic field, providing clues about the planet’s internal structure and composition. These measurements are essential for understanding the processes that have shaped Mercury over time and how it compares to other rocky planets in the solar system.
As scientists continue to analyze the data collected by the spacecraft, they are optimistic about the potential discoveries that lie ahead. The detailed images and measurements will not only enhance our understanding of Mercury but also contribute to broader questions about planetary formation and evolution in the solar system. The mission represents a significant advancement in planetary science, showcasing the capabilities of modern technology in unraveling the mysteries of our celestial neighbors.
In conclusion, the recent capture of detailed images of Mercury’s surface marks a milestone in planetary exploration. The new spacecraft has provided scientists with valuable data that will enhance our understanding of the planet’s geology, atmosphere, and magnetic field. As researchers continue to study the findings, they hope to uncover more about Mercury’s history and its place within the solar system. This mission exemplifies the ongoing quest for knowledge about our universe and the importance of continued exploration of the planets that share our solar neighborhood.